Test and Tag – From Wikipedia
AS/NZS 3760 is a standard created by Standards Australia that outlines a testing method and frequency for electrical appliances. It was created to minimize electrical hazards in the workplace. Appliances are inspected for damage, and various measurements are made to the appliances’ earth continuity, insulation, polarity, and physical condition. After testing has determined a pass, a tag is attached to the appliance lead indicating when it was tested, when the next test is due, and a tracking code. Retesting intervals of equipment can vary from 3 months to 5 years, depending of the environment where the equipment is located.
This standard is used in both Australia and New Zealand. Colloquially, the standard is often referred to as Test and Tag.
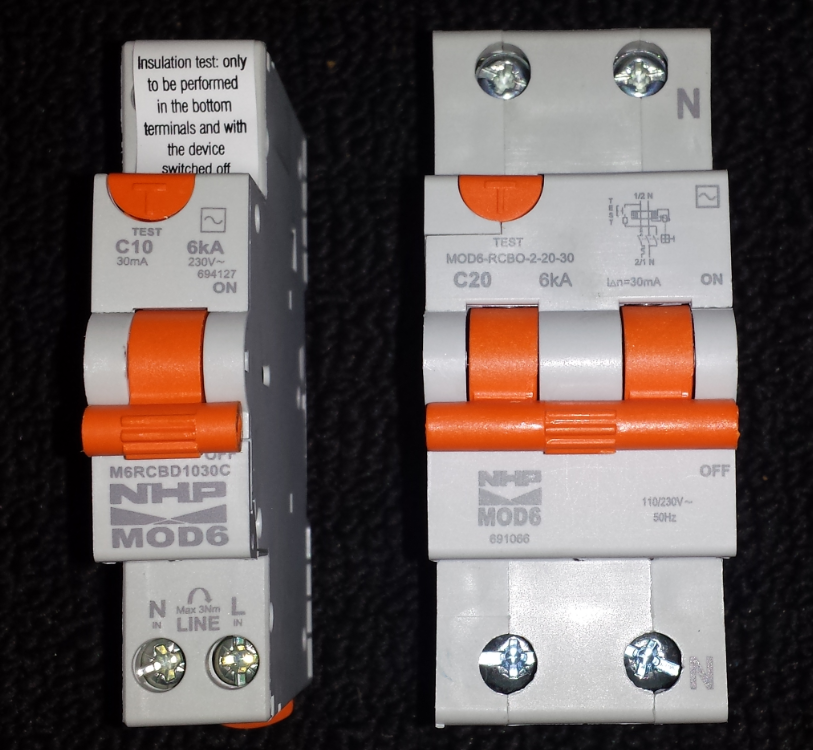
The standard also includes the inspection and testing specifications for RCD’s.
Excluded items:
The items listed below are not included in Standard recommendations:
- Hard or fixed wired
- Exceeding 2.5mtrs in height
- Dismantled items to check operation safety
- New, sample or demo items contained within a warehouse or retail situation


- Rolly’s Electrical Test and Tag
Extension cords or flexible leads
- All employers and self-employed people must locate and protect extension leads and flexible cables so they are not damaged by anything, including liquid. An example is using a cover to prevent crushing or other damage in pedestrian and vehicle areas.
- The following two Electrical Safety Codes of Practice provide valuable information on electrical safety at work:
- Electrical Safety Code of Practice 2010 – Working Near Exposed Live Parts
- Electrical Safety Code of Practice 2010 – Risk Management
Fixed Residual Current Devices (RCD’s) / Safety Switch Testing
RCDs should also be tested on a regular basis. The standard detailing the requirements for these tests is covered in AS/NZS 3760:2010.
The following tests should be carried out:
- Visual
- Mechanical test (check that the RCD trips when pressing the test button)
- Safety switch injection tests (time to trip) – this is where a test current is injected into the RCD protected power point and the time to trip the RCD is measured both at zero degrees and 180 degrees of the sine wave cycle.